Our Network
Resources and Tools
The Comprehensive Guide to Project-Based Learning: Empowering Student Choice through an Effective Teaching Method
In K-12 education, project-based learning (PBL) has gained momentum as an effective inquiry-based, teaching strategy that encourages students to take ownership of their learning journey.
By integrating authentic projects into the curriculum, project-based learning fosters active engagement, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. This comprehensive guide explores the principles, benefits, implementation strategies, and evaluation techniques associated with project-based instruction, highlighting its emphasis on student choice and its potential to revolutionize education.
What is Project-Based Learning?
Project-based learning (PBL) is a inquiry-based and learner-centered instructional approach that immerses students in real-world projects that foster deep learning and critical thinking skills. Project-based learning can be implemented in a classroom as single or multiple units or it can be implemented across various subject areas and school-wide.
In contrast to teacher led instruction, project-based learning encourages student engagement, collaboration, and problem-solving, empowering students to become active participants in their own learning. Students collaborate to solve a real world problem that requires content knowledge, critical thinking, creativity, and communication skills.
Students aren’t only assessed on their understanding of academic content but on their ability to successfully apply that content when solving authentic problems. Through this process, project-based learning gives students the opportunity to develop the real-life skills required for success in today’s world.
Positive Impacts of Project-Based Learning
By integrating project-based learning into the classroom, educators can unlock a multitude of benefits for students. The research evidence overwhelmingly supports the positive impact of PBL on students, teachers, and school communities. According to numerous studies (see Deutscher et al, 2021; Duke et al, 2020; Krajick et al, 2022; Harris et al, 2015) students in PBL classrooms not only outperform non-PBL classrooms academically, such as on state tests and AP exams, but also the benefits of PBL extend beyond academic achievement, as students develop essential skills, including creativity, collaboration, communication, and critical thinking. Additional studies documenting the impact of PBL on K-12 learning are available in the PBL research and in the Benefits of Project-Based Learning resource on the New Tech Network website.
New Tech Network Project-Based Learning Impacts
Established in 1996, New Tech Network NTN is a leading nonprofit organization dedicated to transforming teaching and learning through innovative instructional practices, with project-based learning at its core.
NTN has an extensive network of schools across the United States that have embraced the power of PBL to engage students in meaningful, relevant, and challenging projects, with professional development to support teachers in deepening understanding of “What is project-based learning?” and “How can we deliver high quality project-based learning to all students?”
With over 20 years of experience in project-based learning, NTN schools have achieved impactful results. Several research studies documented that students in New Tech Network schools outperform their peers in non-NTN schools on SAT/ACT tests and state exams in both math and reading (see Hinnant-Crawford & Virtue, 2019; Lynch et al, 2018; Stocks et al, 2019).

NTN provides comprehensive support to educators, including training, resources, and ongoing coaching, to ensure the effective implementation of problem-based learning and project-based learning. Through their collaborative network, NTN continuously shares best practices, fosters innovation, enables replication across districts, and empowers educators to create transformative learning experiences for their students (see Barnett et al, 2020; Hernández et al, 2019). Learn more about Professional Development for Project-Based Learning.
Key Concepts of Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning is rooted in several key principles that distinguish it from other teaching methods. The pedagogical theories that underpin project-based learning and problem-based learning draw from constructivism and socio-cultural learning. Constructivism posits that learners construct knowledge through active learning and real world applications. Project-based learning aligns with this theory by providing students with opportunities to actively construct knowledge through inquiry, hands-on projects, real-world contexts, and collaboration.
Students as active participants
Project-based learning is characterized by learner-centered, inquiry-based, real world learning, which encourages students to take an active role in their own learning. Instead of rote memorization of information, students engage in meaningful learning opportunities, exercise voice and choice, and develop student agency skills. This empowers students to explore their interests, make choices, and take ownership of their learning process, with teachers acting as facilitators rather than the center of instruction.
Real-world and authentic contexts
Project-based learning emphasizes real-world problems that encourage students to connect academic content to meaningful contexts, enabling students to see the practical application of what they are learning. By tackling personally meaningful projects and engaging in hands-on tasks, students develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and its relevance in their lives. Learn more by reading What is Authentic PBL?

Collaboration and teamwork
Another essential element of project-based learning is collaborative work. Students collaborating with their peers towards the culmination of a project, mirrors real-world scenarios where teamwork and effective communication are crucial. Through collaboration, students develop essential social and emotional skills, learn from diverse perspectives, and engage in constructive dialogue.
Project-based learning embodies student-centered learning, real-world relevance, and collaborative work. These principles, rooted in pedagogical theories like constructivism, socio-cultural learning, and experiential learning, create a powerful learning environment, across multiple academic domains, that foster active engagement, thinking critically, and the development of essential skills for success in college or career or life beyond school.
A Unique Approach to Project-Based Learning: New Tech Network
Why Undertake this Work?
New Tech Network schools are committed to these key focus areas: College and Career Readiness, Supportive Culture, Learner-Centered Instruction, and Assessment.
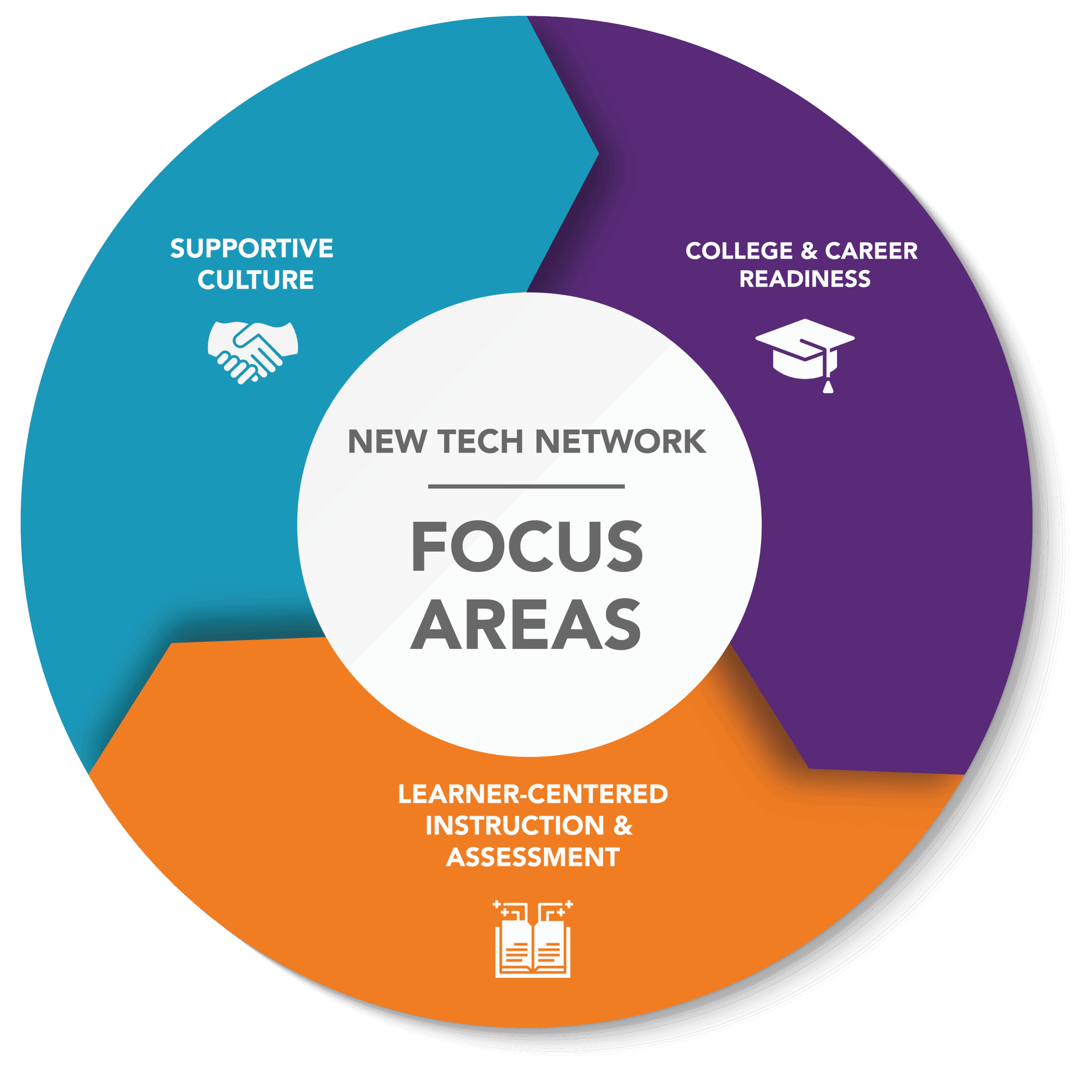 By developing expertise in each of these four domains, schools benefit from discovering the ways each distinct area reinforces the other three. Teachers and school leaders operate in an environment built on a vision and collective action, where educators are the architects of the learning environment. The student experience is tied directly to deeper learning outcomes. Students gain skills and use their voices in ways that prepare them for life beyond school.
By developing expertise in each of these four domains, schools benefit from discovering the ways each distinct area reinforces the other three. Teachers and school leaders operate in an environment built on a vision and collective action, where educators are the architects of the learning environment. The student experience is tied directly to deeper learning outcomes. Students gain skills and use their voices in ways that prepare them for life beyond school.
In the New Tech Network Model, rigorous project-based learning allows students to engage with material in creative, culturally relevant ways, experience it in context, and share their learning with peers.
Teachers, administrators, and district leaders undertake this work because it produces critical thinkers, problem-solvers, and collaborators who are vital to the long-term health and wellbeing of our communities.
Reynoldsburg City Schools (RCS) Superintendent Dr. Melvin J. Brown observed that “Prior to (our partnership with New Tech Network) we were just doing the things we’ve always done, while at the same time, our local industry was evolving and changing— and we were not changing with it. We recognized we had to do better to prepare kids for the reality they were going to walk into after high school and beyond.
Students embrace the Model because they feel a sense of belonging. They are challenged to learn in relevant, meaningful ways that shape the way they interact with the world, like these students from Owensboro Innovation Academy in Owensboro, Kentucky.
When change is collectively held and supported rather than siloed, and all stakeholders are engaged rather than alienated, schools and districts build their own capacity to sustain innovation and continuously improve. New Tech Network’s approach to change provides teachers, administrators, and district leaders with clear roles in adopting and adapting student-centered learning.

Part of NTN’s process for equipping schools with the data they need to serve their students involves conducting research surveys about their student’s experiences.
“The information we received back from our NTN surveys about our kids’ experiences was so powerful,” said Amanda Ziaer, Managing Director of Strategic Initiatives for Frisco ISD. “It’s so helpful to be reminded about these types of tactics when you’re trying to develop an authentic student-centered learning experience. It’s just simple things you might skip because we live in such a traditional adult-centered world.”
NTN’s experienced staff lead professional development activities that enable educators to adapt to student needs and strengths, and amplify those strengths while adjusting what is needed to address challenges.
Meaningful and Equitable Instruction
The New Tech Network model is centered on a PBL instructional core. PBL as an instructional method overlaps with key features of equitable pedagogical approaches including student voice, student choice, and authentic contexts. The New Tech Network model extends the power of PBL as a tool for creating more equitable learning by building asset-based equity pedagogical practices into the the design using key practices drawn from the literature on culturally sustaining teaching methods so that PBL instruction leverages the assets of diverse students, supports teachers as warm demanders, and develops critically conscious students in PBL classrooms (see Good teaching, warm and demanding classrooms, and critically conscious students: Measuring student perceptions of asset-based equity pedagogy in the classroom).
Examples of Project-Based Learning
The NTN Project Planning Toolkit is used as a guide in the planning and design of PBL. This project-based learning lesson plan template or Project Planning Toolkit sample can be used as a resource for project planning from ideation to scaffolding and beyond. Download and use the toolkit as a teaching tool for how to plan a project and to create a solid project plan, ready to implement in the classroom. For ideas and sample lesson plans of projects across grade levels and content areas see the resources below:
The Role of Technology in Project-Based Learning
A tool for creativity
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing PBL in schools, facilitating student engagement, collaboration, and access to information. At the forefront, technology provides students with tools and resources to research, analyze data, and create multimedia content for their projects.

A tool for collaboration
Technology tools enable students to express their understanding creatively through digital media, such as videos, presentations, vlogs, blogs and interactive websites, enhancing their communication and presentation skills.
A tool for feedback
Technology offers opportunities for authentic audiences and feedback. Students can showcase their projects to a global audience through online platforms, blogs, or social media, receiving feedback and perspectives from beyond the classroom. This authentic audience keeps students engaged and striving for high-quality work and encourages them to take pride in their accomplishments.
By integrating technology into project-based learning, educators can enhance student engagement, deepen learning, and prepare students for a digitally interconnected world.
Interactive PBL Resources
New Tech Network offers a wealth of resources and articles to support educators in gaining a deeper understanding of project-based learning. One valuable tool is the NTN Help Center, which provides comprehensive articles and resources on the principles and practices of implementing project-based learning.
The image clarifies the difference between the traditional education approach of “doing projects” and true project-based learning.
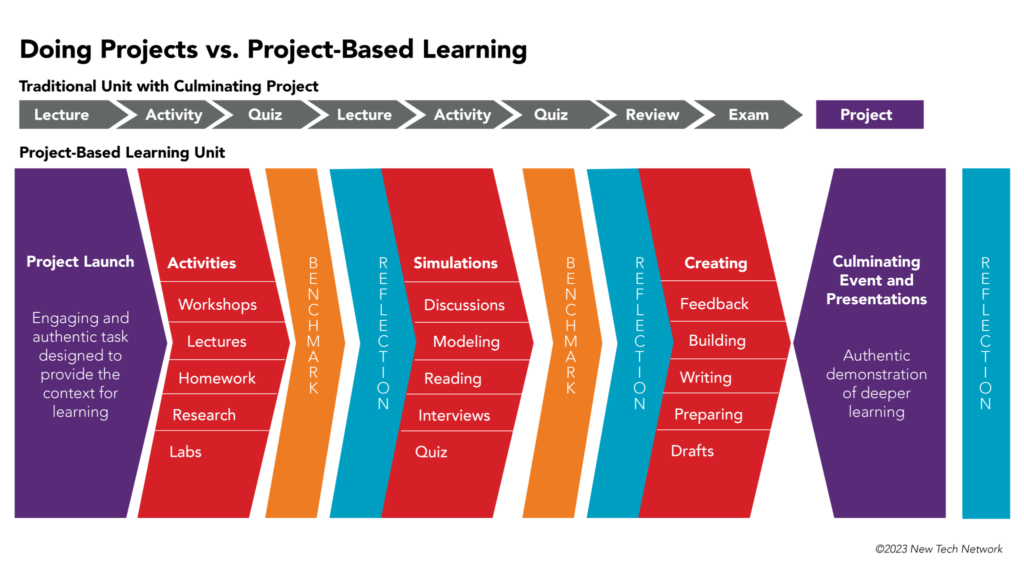
Project Launch
Students are introduced to a project by an Entry Event in the Project Launch (designated in purple on the image) this project component typically requires students to take on a role beyond that of ‘student’ or ‘learner’. This occurs either by placing students in a scenario that has real world applications, in which they simulate tasks performed by adults and/or by requiring learners to address a challenge or problem facing a particular community group.
The Entry Event not only introduces students to a project but also serves as the “hook” that purposefully engages students in the launch of a project. The Entry Event is followed by the Need to Know process in which students name what they already know about a topic and the project ask and what they “need to know” in order to solve the problem named in the project. Next steps are created which support students as they complete the Project Launch phase of a project.
Scaffolding
Shown in the image in red, facilitators ensure students gain content knowledge and skills through ‘scaffolding’. Scaffolding is defined as temporary supports for students to build the skills and knowledge needed to create the final product. Similar to scaffolding in building construction, it is removed when these supports are no longer needed by students.
Scaffolding can take the form of a teacher providing support by hosting small group workshops, students engaging in independent research or groups completing learner-centered activities, lab investigations, formative assessments and more.
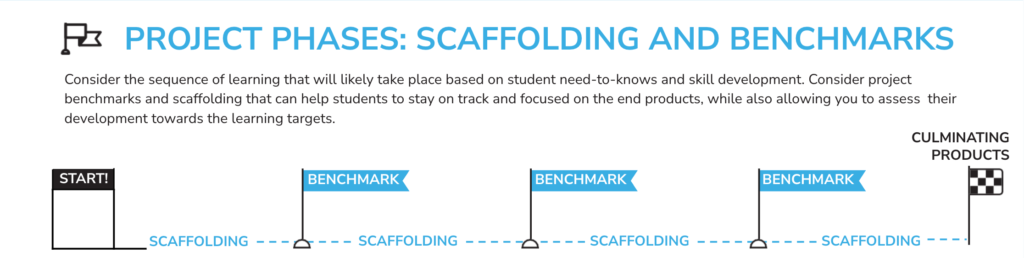
Benchmarks
Benchmarks (seen in orange in the image) can be checks for understanding that allow educators to give feedback on student work and/or checks to ensure students are progressing in the project as a team. After each benchmark, students should be given time to reflect on their individual goals as well as their team goals. Benchmarks are designed to build on each other to support project teams towards the culminating product at the end of the project. To learn more about scaffolding and benchmarks read Scaffolding in Teaching: Supporting Student Success Through Project-Based Learning.
Educators can refer to this resource to gain insights into best practices, instructional strategies, and classroom management techniques that foster an engaging and effective project-based learning environment.
From understanding the principles and practices of PBL to accessing examples of a particular project, evaluating project quality, and exploring effective teaching and learning strategies, educators can leverage these resources to enhance their PBL instruction and create meaningful learning experiences for their students.
Preparing Students for the Future with PBL
The power of PBL is the way in which it encourages students to think critically, collaborate, and sharpen communication skills, which are all highly sought-after in today’s rapidly evolving workforce. By engaging in authentic, real-world projects, and collaborating with business and community leaders and community members, students develop the ability to tackle complex problems, think creatively, and adapt to changing circumstances.

These skills are essential in preparing students for the dynamic and unpredictable nature of the future job market, where flexibility, innovation, and adaptability are paramount.
“Joining New Tech Network provides us an opportunity to reframe many things about the school, not just PBL,” said Patrick Malley, long time NTN educator and leader. “Eliminating the deficit mindset about kids is the first step to establishing a culture that makes sure everyone in that school is focused on next-level readiness for these kids.”
The New Tech Network Learning Outcomes align with the qualities companies are looking for in new hires: Knowledge and Thinking, Oral Communication, Written Communication, Collaboration and Agency.
NTN schools prioritize equipping students with the necessary skills and knowledge to pursue postsecondary education or training successfully. By integrating college readiness and career readiness into the fabric of PBL, NTN ensures that students develop the academic, technical, and professional skills needed for future success.
Through authentic projects, students learn to engage in research, analysis, and presentation of their work, mirroring the expectations and demands of postsecondary education and the workplace. NTN’s commitment to college and career readiness ensures that students are well-prepared to transition seamlessly into higher education or enter the workforce with the skills and confidence to excel in their chosen paths.
The Impact of PBL on College and Career Readiness
PBL has a profound impact on college and career readiness. Numerous studies document the academic benefits for students, including performance in AP courses, SAT/ACT tests, and state exams (see Deutscher et al, 2021; Duke et al, 2020; Harris et al, 2015). New Tech Network schools demonstrate higher graduation rates and college persistence rates than the national average as outlined in the New Tech Network Impact Report. Over 95% of NTN graduates reported feeling prepared for the expectations and demands of college.
Practices that Support Equitable College Access and Readiness
According to a literature review conducted by New York University’s Metropolitan Center for Research on Equity and the Transformation of Schools (Perez et al, 2021) classroom level, school level, and district level practices can be implemented to create more equitable college access and readiness and these recommendations align with many of the practices built into the the NTN model, including culturally sustaining instructional approaches, foundational literacy, positive student-teacher relationships, and developing shared asset-based mindsets.
About New Tech Network
New Tech Network is committed to meeting schools and districts where they are and helping them achieve their vision of student success. For a full list of our additional paths to impact or to speak with someone about how the NTN Model can make an impact in your district, please send an email to inquiry@newtechnetwork.org.


